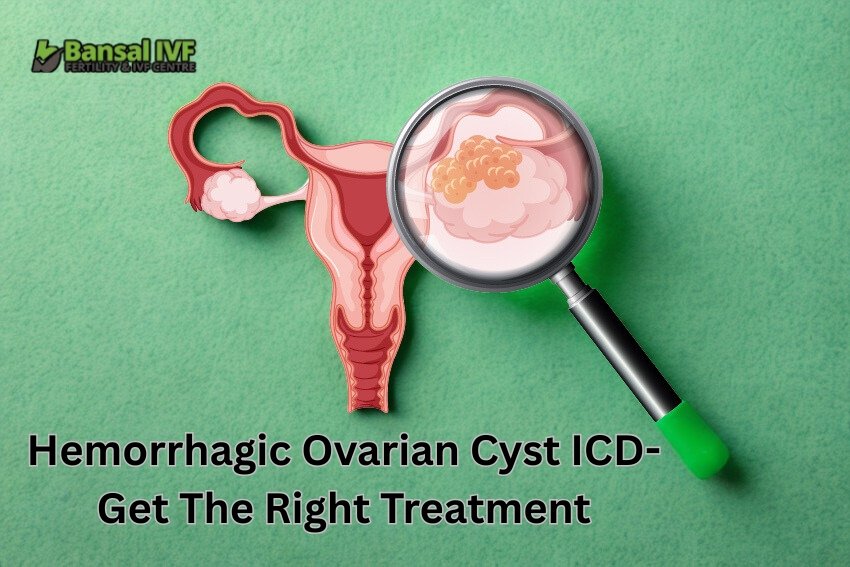
Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cyst is quite frequent among women in their reproductive years, despite the fact that it may appear alarming. When a blood artery inside a functioning ovarian cyst bursts, blood seeps into the cyst,. That eventually is resulting in a hemorrhagic ovarian cyst. Hemorrhagic cysts are usually benign and go away on their own. But, occasionally they can cause pain, problems or necessitate medical attention.
It’s important to understand ovarian cysts, recognize the symptoms of an ovarian cyst rupture, and know when to call your doctor to obtain the care you may need. This article provides a comprehensive overview of ovarian cyst symptoms, causes, and considerations to assist women better understand when they need to seek help by the experts at IVF Centre in Sonipat.
What is Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cyst ICD?

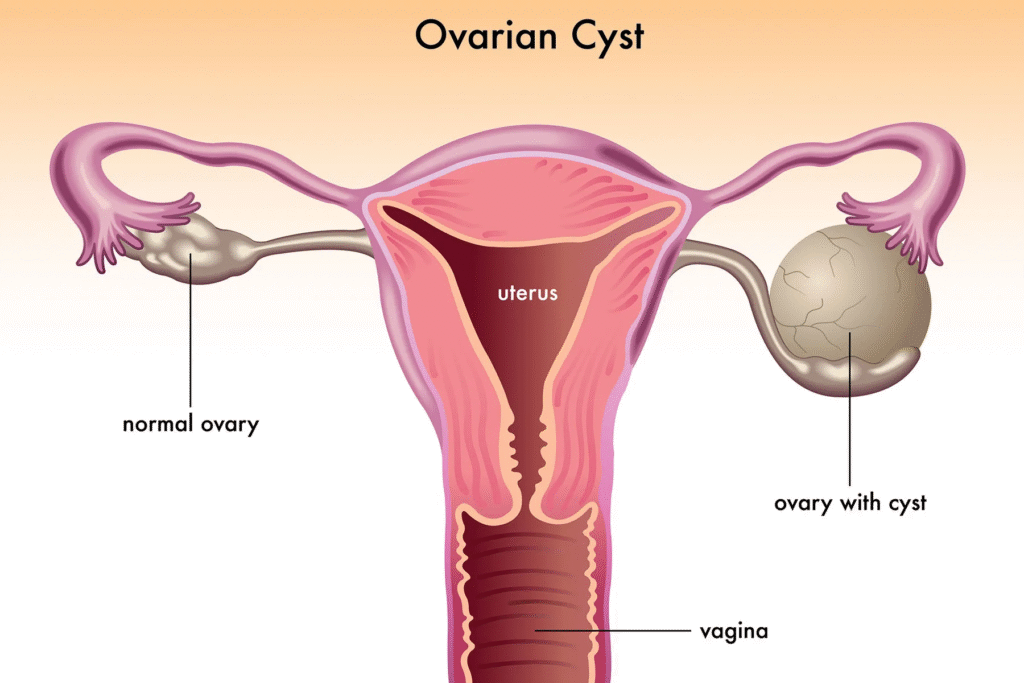
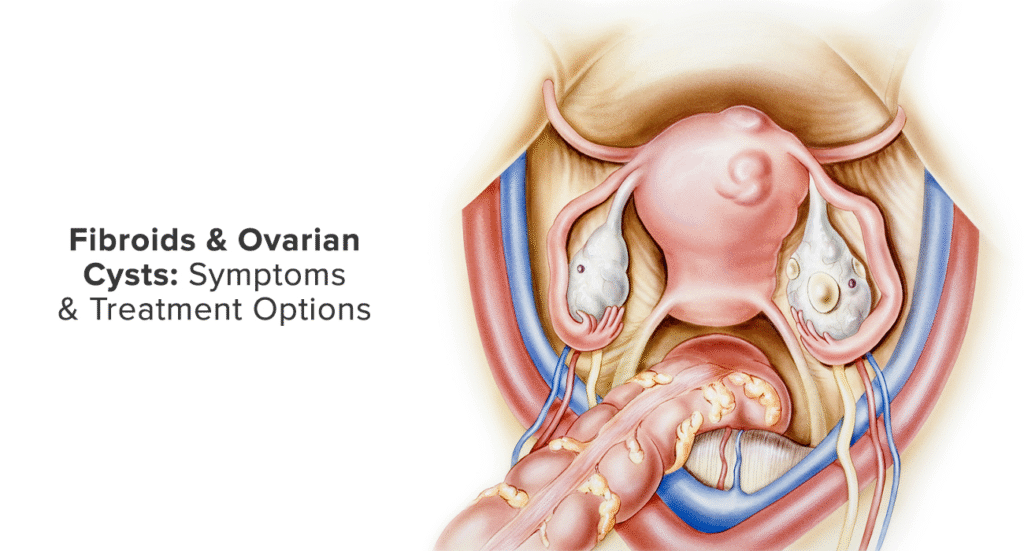
One or both ovaries may develop an ovarian cyst, which is a sac-like structure having fluid in it. The fallopian tubes and other regions close to the ovaries may also develop a cyst. There are ovarian cysts that contain blood. Hematomas or Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cyst ICD are the names that comes in use for these blood-filled cysts.
Although that might sound concerning, the majority of these cysts are benign and never pose a threat. They may, however, occasionally result in pelvic pain or consequences from the cyst rupturing or bleeding heavily. A lady should call her doctor if she is in discomfort and bleeding.
• Hormonal fluctuations during ovulation: Some functional cysts may result from the constantly fluctuating hormone levels during the ovulation cycle. They develop into hemorrhagic cysts if they bleed internally.
• Blood vessel rupture inside a cyst: Pain and swelling may result from bleeding into an existing cyst if a tiny blood vessel bursts inside it.
• More prevalent in women of reproductive age: Because of their busy cycles and continuous ovulation, women in their reproductive years are more susceptible to hemorrhagic ovarian cysts.
• Using fertility treatments may raise the risk: Women who take drugs that stimulate the ovaries may be more susceptible to Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cyst due to the possibility of cyst formation or bleeding.
How Is Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cyst Disgnosis Takes Place?
• Pelvic ultrasonography: This is the main method for identifying the size, location, and presence of internal bleeding in ovarian cysts.
• Blood tests: These check for infections, monitor hormone levels, and determine whether anemia from a bleeding ovarian cyst is the cause.
• Physical examination: To rule in or rule out a hemorrhagic cyst, the physician will look for pain and swelling in the abdomen or pelvis.
If the diagnosis is done on time and the right treatment for Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cyst ICD is given, it will eventually help in avoiding the complications from internal bleeding.
What Are The Treatment Options For Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cyst?
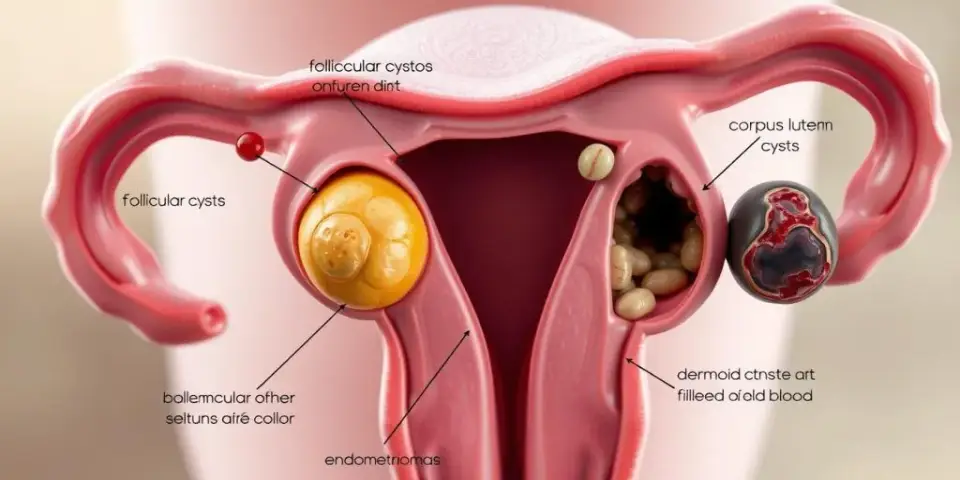
Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cyst depends on the size of the cyst, symptoms and complications that can get affected and how it is treated. The majority of cases are managed conservatively; some will need medication or surgery.
1. Observation and Monitoring:
- Small cysts with minor symptoms are typically treated and they can even go away without any treatment.
- To find out if it has shrunk or vanished, an ultrasound follows up after a few weeks.
- Over-the-counter painkillers like ibuprofen or paracetamol based on your symptoms can also help.
2. Medications:
- Recommended medicines are Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory that are suitable choices for treating pelvic pain and inflammation.
- Hormonal birth control pills may also be taken into consideration to prevent the development of additional cysts.
3. Surgical Intervention:
- Some doctors also give advice to take the laparoscopic cyst removal process if the cyst is large, chronic or is causing some severe discomfort.
- If there is internal bleeding or ovarian torsion results from the cyst rupturing, emergency laparoscopic surgery will be required.
- Part of the ovary may need to be removed in rare instances of tissue damage.
Timely Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cyst ICD treatment helps in avoiding all the complications and ensures that your reproductive health is taken care of.
When It Is Advisable To Have Doctor’s Help For Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cyst?
It’s critical to pay attention to your body’s signals and not ignore any that can point to a ruptured or troublesome cyst.
Get help right away if you encounter:
- Abdominal or pelvic discomfort that comes on suddenly and intensely; weakness, lightheadedness, or fainting (which could be an indication of internal bleeding)
- Pain associated with fever or vomiting
- Prolonged irregular bleeding or pain throughout cycles
- Low blood pressure or a fast heartbeat
A bleeding Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cyst ICD that has ruptured and is urgent is a medical emergency.
What Are The Prevention Tips For Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cyst?
It is hard to stop ovarian cysts from rupturing or leaking, there are few prevention tips that can help in reducing your risk and know about them early:
- Get the pelvic ultrasound and routine gynaecological examinations.
- Monitor your period and ovulation patterns regularly.
- To help suppress ovulation, talk to your doctor about using chemical birth control.
- If you are prone to cysts, it is important to stay away from high-impact activities during ovulation.
- Treating underlying diseases such as endometriosis or PCOS.
- Preserving a healthy lifestyle and a balanced diet to promote reproductive health.
Proactive treatment can reduce the chance of complications and assist in identifying any problems early.
Conclusion:
A Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cyst may sound unpleasant, but as long as you are aware of them early and receive treatment, they are usually not harmful. Eventually, they disappear on their own, but occasionally, medication is needed to manage them. To get to know about the cysts, surgical removal can be recommended. It is important to get the doctor’s advice if you suffer from any of the signs of ovarian cysts.
To give advice to women who confidently take charge of their fertility, Bansal IVF in Sonipat provides specialists in treating ovarian cysts and other reproductive health issues.